3rd Test
Autonomous Navigation with Pathfinding Algorithm (ROS2 + Gazebo)
🎯 Objectives • 📝 Summary • 🧰 Tools • ⚙️ Installation • 📐 Algorithm • 🎮 Simulation • 📊 Results • 📚 Resources
🎯 Objectives
The goal is to build an autonomous navigation system using ROS2 and Gazebo for the TekBot robot. Tasks:
- Implement a pathfinding algorithm (A*, Dijkstra, or RRT)
- Handle obstacle avoidance
- Simulate in Gazebo and visualize with RViz2
📝 Summary
This ROS2 project implements a complete autonomous navigation pipeline for the TekBot robot in a simulated maze environment. It integrates a pathfinding algorithm to compute the optimal route between two points while dynamically avoiding obstacles. The solution is fully tested in Gazebo and visualized in RViz2, showcasing real-time decision-making and obstacle handling.
📁 Project Structure
tekbot_ws/src/tekbot_pathfinding/
├── config/
│ ├── nav2_config.rviz
│ └── nav2_params.yaml
├── launch/
│ └── pathfinding.launch.py
├── tekbot_pathfinding/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── path_planner.py
├── package.xml
├── setup.py
🧰 Tools & Requirements
| Tool | Version |
|---|---|
| ROS2 | Humble Hawksbill |
| OS | Ubuntu 22.04 |
| Simulator | Gazebo |
| Visualizer | RViz2 |
| SLAM | SLAM Toolbox |
| Robot | TekBot |
⚙️ Installation & Configuration
1. Clone environment
git clone https://github.com/charif-tekbot/tekbot_sim.git
cd tekbot_sim
colcon build
source install/setup.bash
2. Launch robot in Gazebo
ros2 launch maze_solving tekbot_maze.launch.py
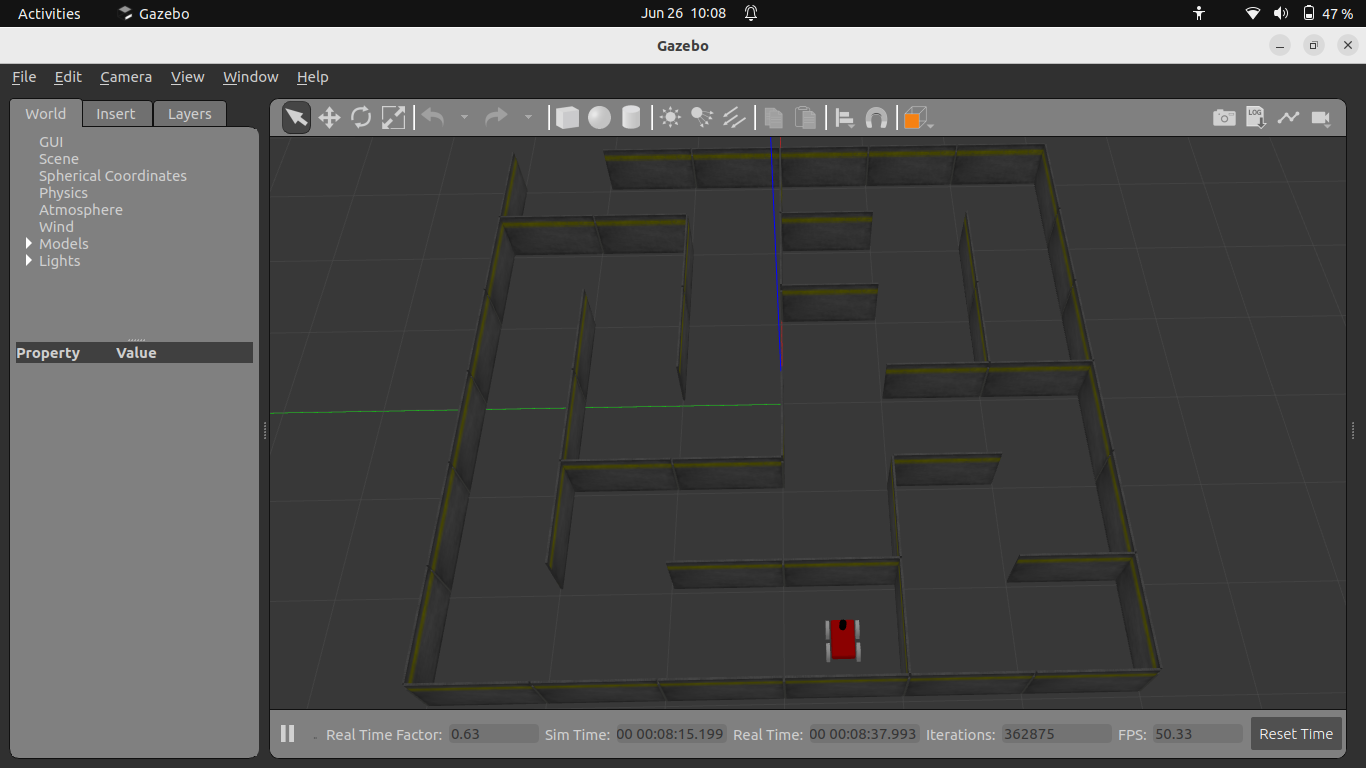
Figure 1: Robot visualization in Gazebo
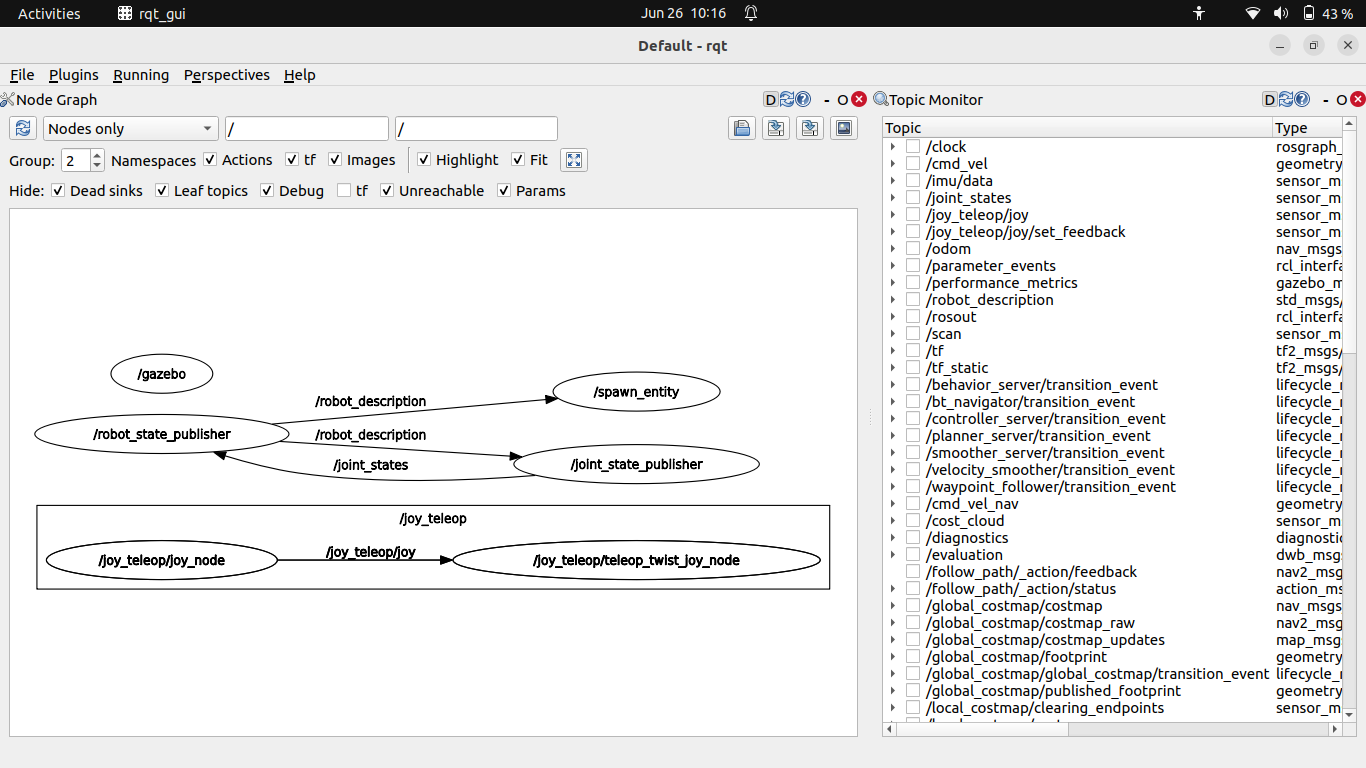
Figure 2: RQT interface for robot control
📐 Algorithm & Implementation
🗺️ Step 1 – Generate the map using SLAM Toolbox
To enable autonomous navigation, we first generated a 2D map using slam_toolbox while driving the robot through the maze.
After launching the robot and the simulation environment in Gazebo:
ros2 launch maze_solving tekbot_maze.launch.py
Then launch the Navigation Stack (Nav2):
ros2 launch nav2_bringup navigation_launch.py use_sim_time:=true
Start SLAM Toolbox to build the map in real time:
ros2 launch slam_toolbox online_async_launch.py use_sim_time:=true
Open RViz2 with the default Nav2 configuration:
ros2 run rviz2 rviz2 -d /opt/ros/humble/share/nav2_bringup/rviz/nav2_default_view.rviz
After disabling the Global Planner and Controller plugins in RViz, we obtain the following view:
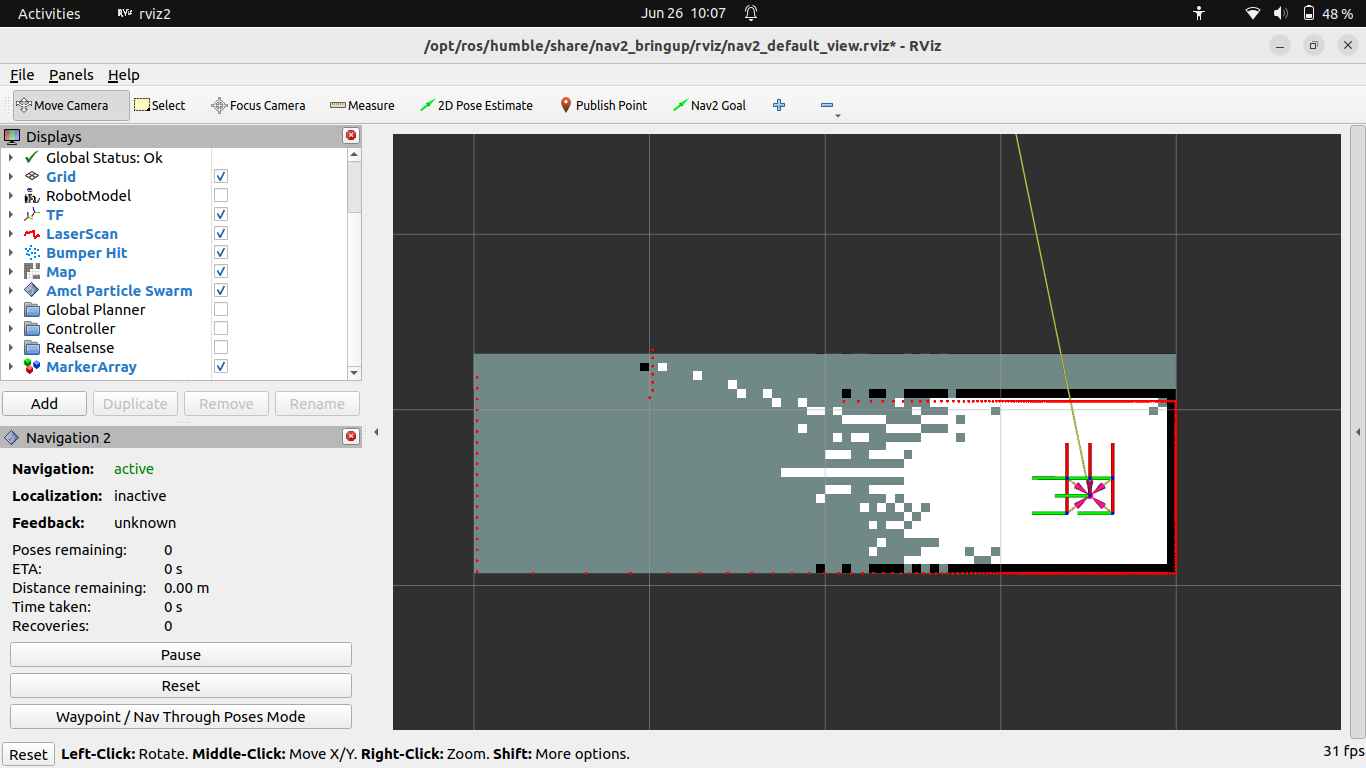
Figure 3: RViz interface showing the mapping process
Use the following command to manually move the robot in the environment using the keyboard:
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard
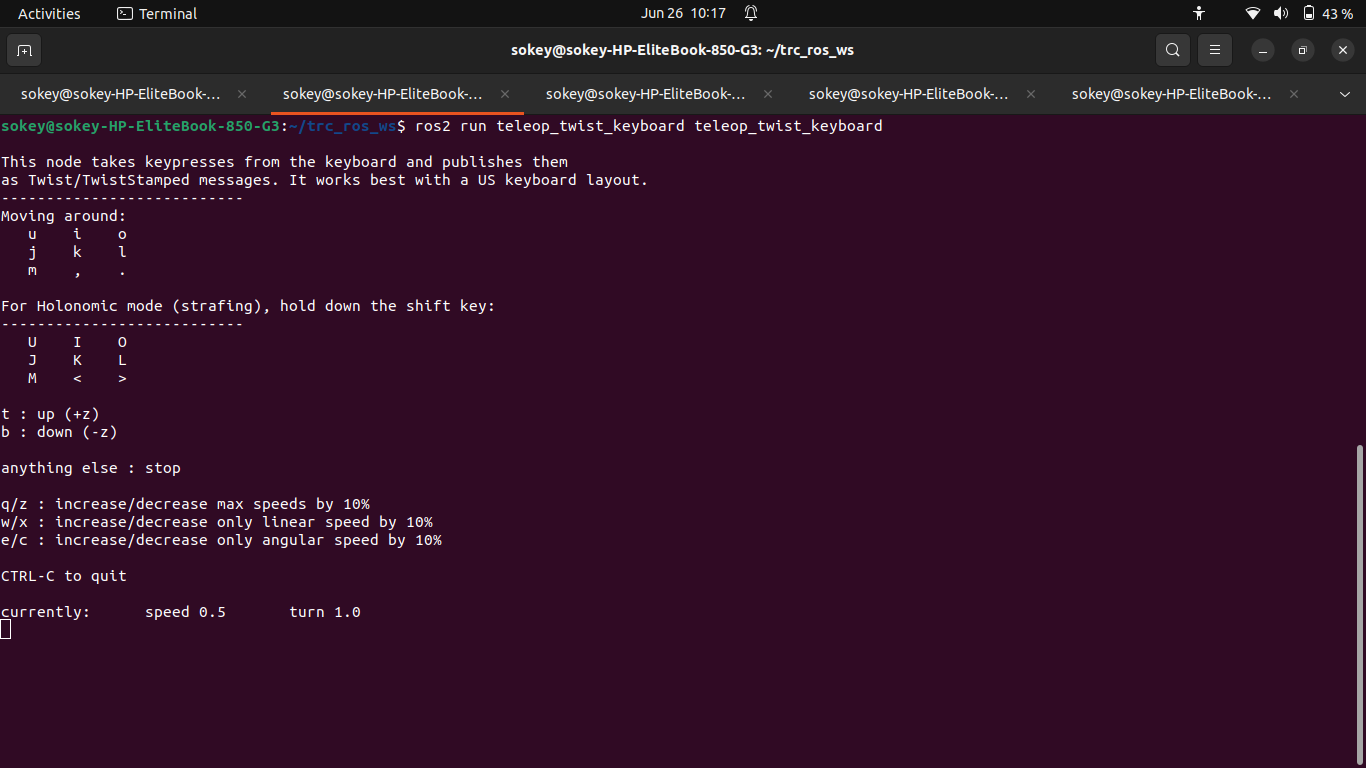
Figure 4: Terminal window for teleoperation commands
Now we use keyboard keys to manually control the robot as it explores the maze, o to move forward, m to move backwar, j to rotate left, l to rotate right. As the robot navigates through the environment, the map is progressively built and visualized in real-time within RViz.
Once the environment has been sufficiently explored, save the generated map:
ros2 run nav2_map_server map_saver_cli -f my_map
Figure 5: Map generated by SLAM Toolbox (white = free, black = occupied, gray = unknown)
Figure 6: YAML file associated with the map, containing metadata and the path to the image file.
Explanation of the my_map.yaml file:
This YAML file contains the necessary information for ROS2 to use the generated map. It includes:
- The path to the map image (usually a PNG or PGM file)
- The map resolution (meters/pixel)
- The origin of the map in the world frame
- Thresholds to distinguish free and occupied areas
- The mode for interpreting the map (e.g., trinary)
This file allows the map server (map_server) to correctly load the map for autonomous navigation.
🤖 Step 2 – Implement the autonomous navigation system
We implemented an A* pathfinding algorithm on top of the generated occupancy grid. Below are the main components of the implementation.
🧠 Nav 2 Paramaters
Voir plus...
controller_server:
ros__parameters:
controller_frequency: 10.0
max_x_velocity: 0.5
xy_goal_tolerance: 0.25
use_sim_time: False
Explanation:
This YAML snippet configures the Nav2 controller server.
controller_frequencysets how often the controller runs (10 Hz).max_x_velocitylimits the robot's maximum linear speed to 0.5 m/s.xy_goal_tolerancedefines how close the robot must get to the goal (0.25 meters).use_sim_timespecifies whether to use simulation time (here, set to false).
📍 A* Pathfinding Lauch
Voir plus...
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
import os
def generate_launch_description():
config_dir = os.path.join(get_package_share_directory('tekbot_pathfinding'), 'config')
return LaunchDescription([
Node(
package='nav2_map_server',
executable='map_server',
name='map_server',
output='screen',
parameters=[{'yaml_filename': os.path.join(config_dir, 'maze.yaml')}]
),
Node(
package='tekbot_pathfinding',
executable='path_planner',
name='path_planner',
output='screen',
parameters=[os.path.join(config_dir, 'nav2_params.yaml')]
),
Node(
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
name='rviz2',
arguments=['-d', os.path.join(config_dir, 'nav2_config.rviz')],
output='screen'
)
])
Explanation:
This launch file starts the main nodes for pathfinding:
- Launches the map server with a specified YAML map file.
- Starts the custom
path_plannernode, which implements the A* algorithm. - Launches RViz2 with a predefined configuration for visualization. It ensures all components needed for autonomous navigation and visualization are started together.
🚦 Path Planner
Voir plus...
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from nav_msgs.msg import OccupancyGrid, Path
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped, Twist
import numpy as np
import heapq
import math
class AStarPlanner(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('a_star_planner')
# Subscriptions
self.create_subscription(OccupancyGrid, '/map', self.map_callback, 10)
self.create_subscription(PoseStamped, '/goal_pose', self.goal_callback, 10)
# Publishers
self.path_pub = self.create_publisher(Path, '/plan', 10)
self.cmd_vel_pub = self.create_publisher(Twist, '/cmd_vel', 10)
# Variables
self.map_data = None
self.robot_pose = [0.0, 0.0] # x, y
def map_callback(self, msg):
"""Stocke la carte en mémoire"""
self.map_data = msg
self.get_logger().info(f"Carte chargée (résolution: {msg.info.resolution} m/pixel)")
def goal_callback(self, msg):
"""Exécute A* quand un nouveau goal arrive"""
if self.map_data is None:
self.get_logger().warn("Carte non initialisée !")
return
start = self.robot_pose
goal = [msg.pose.position.x, msg.pose.position.y]
path = self.a_star(start, goal)
self.publish_path(path)
def a_star(self, start, goal):
"""Implémentation complète de A*"""
grid = np.array(self.map_data.data).reshape(
(self.map_data.info.height, self.map_data.info.width))
start_px = self.world_to_pixel(start)
goal_px = self.world_to_pixel(goal)
open_set = []
heapq.heappush(open_set, (0, start_px))
came_from = {}
g_score = {start_px: 0}
f_score = {start_px: self.heuristic(start_px, goal_px)}
while open_set:
current = heapq.heappop(open_set)[1]
if current == goal_px:
return self.reconstruct_path(came_from, current)
for neighbor in self.get_neighbors(current, grid):
tentative_g_score = g_score[current] + 1
if neighbor not in g_score or tentative_g_score < g_score[neighbor]:
came_from[neighbor] = current
g_score[neighbor] = tentative_g_score
f_score[neighbor] = tentative_g_score + self.heuristic(neighbor, goal_px)
heapq.heappush(open_set, (f_score[neighbor], neighbor))
self.get_logger().warn("A* : Pas de chemin trouvé !")
return []
def get_neighbors(self, pos, grid):
"""Retourne les voisins valides (4-connexité)"""
neighbors = []
for dx, dy in [(0,1), (1,0), (0,-1), (-1,0)]:
x, y = pos[0] + dx, pos[1] + dy
if 0 <= x < grid.shape[0] and 0 <= y < grid.shape[1]:
if grid[x, y] < 50: # Seuil d'obstacle
neighbors.append((x, y))
return neighbors
def heuristic(self, a, b):
"""Distance de Manhattan"""
return abs(a[0] - b[0]) + abs(a[1] - b[1])
def reconstruct_path(self, came_from, current):
"""Reconstruit le chemin depuis le goal"""
path = [current]
while current in came_from:
current = came_from[current]
path.append(current)
path.reverse()
return [self.pixel_to_world(p) for p in path]
def world_to_pixel(self, world_pos):
"""Convertit les coordonnées réelles -> indices de grille"""
return (
int((world_pos[0] - self.map_data.info.origin.position.x) / self.map_data.info.resolution),
int((world_pos[1] - self.map_data.info.origin.position.y) / self.map_data.info.resolution)
)
def pixel_to_world(self, pixel_pos):
"""Convertit les indices -> coordonnées réelles"""
return (
pixel_pos[0] * self.map_data.info.resolution + self.map_data.info.origin.position.x,
pixel_pos[1] * self.map_data.info.resolution + self.map_data.info.origin.position.y
)
def publish_path(self, path):
"""Publie le chemin dans RViz"""
path_msg = Path()
path_msg.header.frame_id = 'map'
for point in path:
pose = PoseStamped()
pose.pose.position.x = point[0]
pose.pose.position.y = point[1]
path_msg.poses.append(pose)
self.path_pub.publish(path_msg)
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
planner = AStarPlanner()
rclpy.spin(planner)
planner.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Explanation:
This Python node implements the A* pathfinding algorithm:
- Subscribes to the map and goal topics.
- When a goal is received, it computes the shortest path on the occupancy grid using A*.
- Publishes the planned path for visualization in RViz2.
- Converts between world and grid coordinates, checks for obstacles, and reconstructs the path from start to goal. This node is the core of autonomous navigation, enabling the robot to plan and follow optimal paths in the environment.
🎮 Simulation & Visualization
The system was tested inside the tekbot_maze.world file using Gazebo. RViz2 was used to visualize the robot, the map, and the planned path in real time.
📊 Results & Analysis
| Scenario | Expected Outcome | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Path planning | Shortest path found | ✅ Success |
| Obstacle in direct path | Alternate path selected | ✅ Success |
| Simulation launch | Environment starts properly | ✅ Success |
| Visualization | Path visible in RViz2 | ✅ Success |
🐞 Error Log
| Date | Error encountered | Cause | Solution provided |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23/06/2025 | Error generating the map with slam_toolbox | The environment variable was set to Cyclone DDS instead of Fast DDS. | Changed the environment variable to use Fast DDS (export RMW_IMPLEMENTATION=rmw_fastrtps_cpp). |
📚 Resources
- https://docs.ros.org/en/humble/index.html
- https://husarion.com/tutorials/ros2-tutorials/ros2/
- https://github.com/charif-tekbot/tekbot_sim
- https://gazebosim.org/docs
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A*_search_algorithm
👥 Authors
- Agbodja Marzoukath
- Ife Leonce Comlan
- Chatigre Larissa
Test 3 - Tekbot Robotics Challenge
Date: June 2025
Language: Python 3 / ROS2
Framework: ROS2 Humble
© 2025 Tekbot Robotics Challenge. All rights reserved.
Framework: ROS2 Humble
© 2025 Tekbot Robotics Challenge. All rights reserved.